
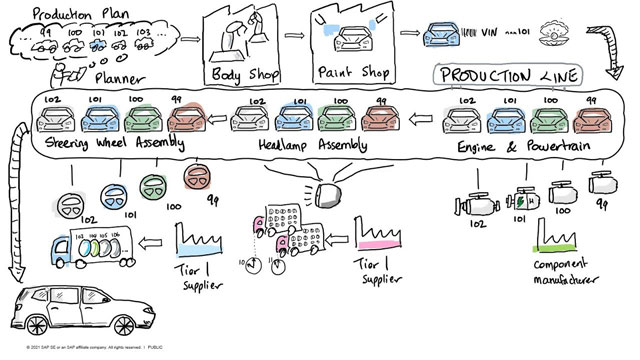
Automotive supply chain between tier 1 component suppliers and OEMs.
The automotive supply chain between tier 1 component suppliers and OEMs (Original Equipment Manufacturers) is a complex network that involves multiple stakeholders and processes. Tier 1 component suppliers are typically large companies that provide complex systems or modules to the OEMs, such as engines, transmissions, and electronic control modules. In this article, we will explain the key aspects of the automotive supply chain between tier-1 component suppliers and OEMs.
Planning and Forecasting:
The automotive supply chain begins with planning and forecasting by the OEMs and tier 1 component suppliers. The OEMs provide forecasts of their production requirements to the tier 1 suppliers, who then use this information to plan their production and delivery schedules. This planning process is critical to ensure that the tier 1 suppliers can meet the OEMs' production requirements. Procurement: Once the production requirements are established, the tier 1 suppliers begin procuring the raw materials and components necessary to manufacture their products. This involves working with suppliers of raw materials and components, negotiating prices, and managing inventory levels to ensure that they have the necessary materials to meet the OEMs' production schedules.

Manufacturing:
The tier 1 suppliers manufacture the components or systems based on the OEMs' requirements. This involves managing the production process, ensuring quality control, and meeting delivery schedules. The components or systems are typically shipped to the OEMs' manufacturing facilities for assembly.

Inbound Logistics:
Inbound logistics involves the transportation of the components or systems from the tier 1 suppliers to the OEMs' manufacturing facilities. This includes the selection of transportation modes, such as truck, rail, or air, and the management of transportation schedules to ensure that the components arrive at the manufacturing facilities on time.
Assembly:
The components or systems are assembled at the OEMs' manufacturing facilities into finished vehicles. This involves managing the assembly process, ensuring quality control, and meeting delivery schedules.

Outbound Logistics:
Outbound logistics involves the transportation of the finished vehicles from the manufacturing facilities to dealerships or customers. This includes the selection of transportation modes, such as truck, rail, or sea, and the management of transportation schedules to ensure that the vehicles are delivered to their destination on time.

Aftermarket:
The automotive supply chain also involves the aftermarket, which includes the maintenance, repair, and replacement of components and systems. This involves managing the distribution of replacement parts and components, providing support to dealerships and customers, and managing warranties and returns.

In summary, the automotive supply chain between tier 1 component suppliers and OEMs involves planning and forecasting, procurement, manufacturing, inbound logistics, assembly, outbound logistics, and aftermarket activities. Effective management of these activities is critical to ensure that the components and systems are delivered on time, meet quality standards, and support the production of high-quality vehicles.






Leave a reply